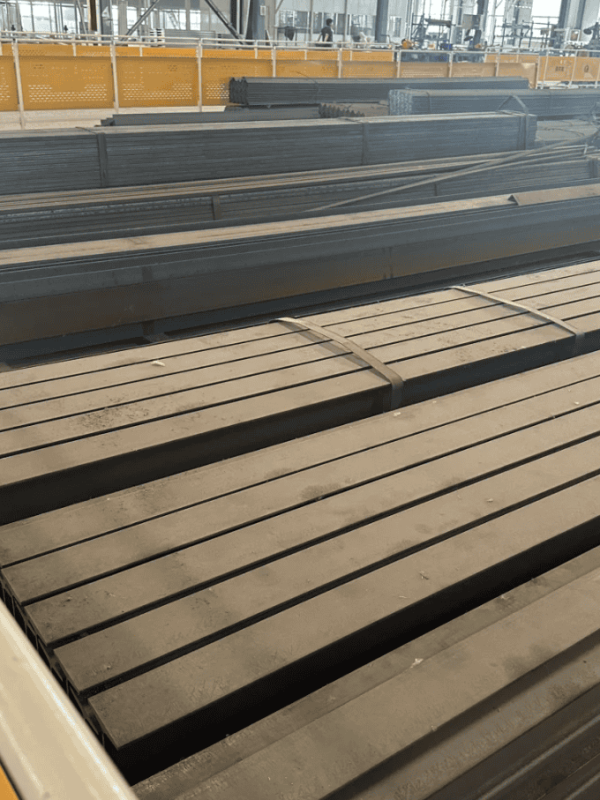
Introduction to Bridge Steel
Bridge steel is a type of steel made specifically for building bridges, known for its strength and ability to handle heavy loads. It typically has a yield strength between 250 and 485 MPa (36 to 70 ksi) and a tensile strength from 400 to 620 MPa (58 to 90 ksi). These properties allow bridges to be built with less material, making them lighter but still very strong.
Bridge steel is also designed to resist stress, rust, and temperature changes, making it reliable in different climates. There are various grades available, each made for different types of bridge projects, from small footbridges to large highway or railway bridges. This makes bridge steel a long-lasting, safe, and cost-effective choice for construction.
Benefits of Bridge Steel
- High load capacity
- Strong yet lightweight
- Weather-resistant and durable
- Longer lifespan, less maintenance
- Maximizes span with fewer supports
- Cost-effectiveness
- Easy to install

Common Types of Bridge Steel
- Carbon Structural Steel
- Common Grades: A36, S235, Q235
- Applicability: Smaller bridges and light-load structures like beams and supports.
- High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel
- Common Grades: A572 (Grades 50/60/65), S355, Q355
- Applicability: Load-bearing components in medium-sized bridges (trusses, beams, columns).
- Weathering Steel
- Common Grades: A588, Corten A, Corten B
- Applicability: Exposed bridges (highways, railways) requiring corrosion resistance.
- Bridge-Specific Steel
- Common Grades: Q370qC, Q370qD, Q420qD
- Applicability: Large bridges, suitable for main beams and suspension structures under heavy loads.

Industries & Applications
Some common industries and applications include:
Construction

Transportation

Marine
Energy
Mining
Manufacturing

Defense
Agriculture
Bridge Steel Product Specifications
| Grade | Specifications | Standard | ||
| Thickness (mm) | Width (mm) | Length (mm) | ||
| Q345q | 6~100 | 900~4800 | 3000~25000 | GB/T 714 |
| Q370q | ||||
| Q420q | ||||
| Q460q | 8~100 | |||
| Q500qD/E | ||||
| Q345qDNH/ENH | 6~150 | |||
| Q370qDNH/ENH | 6~100 | |||
| Q420qDNH/ENH | 8~80 | |||
| Q460qDNH/ENH | 8~80 | |||
| Q500qDNH/ENH | 8~60 | |||
| A709 Gr.36 | 6~150 | 900~4800 | 3000~25000 | ASTM A709/ A709M |
| A709 Gr.50 | 6~150 | |||
| A709 50W | 6~150 | |||
| A709 HPS 50W | 6~150 | |||
| A709 HPS 70W | 8~100 | |||
Bridge Steel When & Where You Need It
At SteelPRO Group, you get more than just quality steel. With multiple facilities across the country capable of providing bridge steel, we can also work with you to manage your inventory, ensuring you get the product when and where you need it to keep your production running.
Explore Our Available Steel Products & Grades
Our knowledge and experience give nearly 100% accurate delivery of High Carbon, Low Carbon, Stainless Steel products processed and packaged to your exact specifications.















