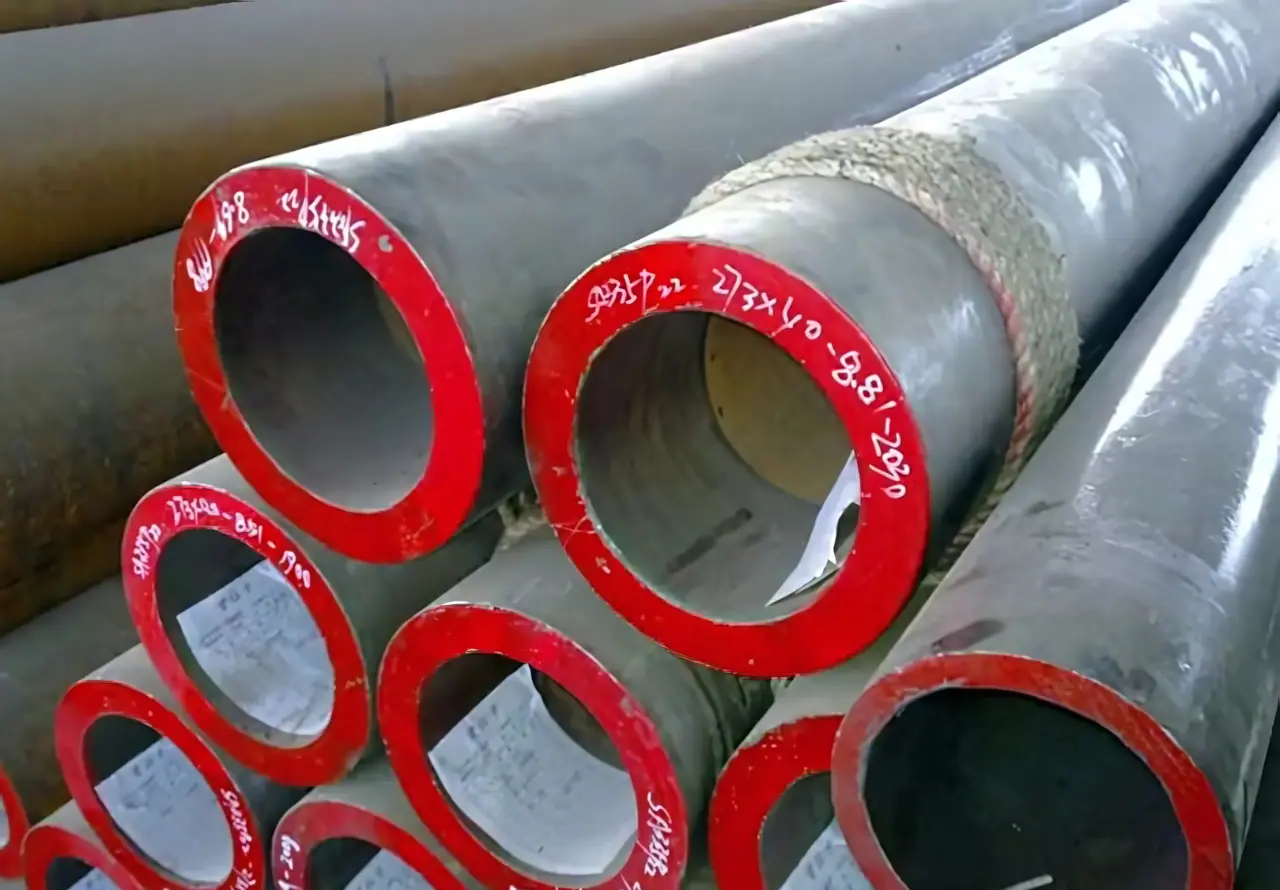
X70 | L485MB | High-Strength Pipeline Steel
X70 | L485MB | High-Strength Pipeline Steel
X70 is a high-strength pipeline steel widely used in the oil and gas industry. It meets the API 5L standard. The “X” signifies its use for pipelines, while “70” refers to its yield strength of 70,000 psi. Equivalent grades include L485M (China) and L485MB (Europe). X70 has high strength, good weldability, and toughness. It is ideal for long-distance, high-pressure pipeline applications.
Description
What Is X70?
X70 is a high-strength pipeline steel composed of approximately 98% iron and 2% carbon and alloying elements. It is typically produced in solid, round, or rectangular shapes and has a silver-gray color. X70 is known for its excellent weldability, toughness, and high yield strength. It is primarily used in the oil and gas industry for long-distance, high-pressure pipelines. The steel is manufactured through hot rolling and can be further classified based on its yield strength and specific applications.
Characteristics of X70
X70 steel is known for its high strength and excellent toughness, making it ideal for pipeline construction, especially in demanding environments. It offers good weldability and resistance to crack propagation, which enhances its reliability. X70 is widely used in long-distance pipelines, where strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness are critical.
While X70 is highly effective, alternative grades like X65 and X80 can be considered. X65 provides slightly lower strength but better flexibility, and X80 offers higher strength for even more demanding applications.Chemical Compositions
| Element | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon, C | 0.04 – 0.06 |
| Manganese, Mn | 1.00 – 1.45 |
| Phosphorus, P | ≤ 0.015 |
| Sulfur, S | ≤ 0.005 |
| Silicon, Si | 0.15 – 0.40 |
| Vanadium, V | 0.03 – 0.06 |
| Niobium, Nb | 0.02 – 0.05 |
| Titanium, Ti | ≤ 0.015 |
| Copper, Cu | ≤ 0.40 |
| Nickel, Ni | ≤ 0.30 |
| Molybdenum, Mo | ≤ 0.15 |
| Chromium, Cr | ≤ 0.30 |
| Aluminum, Al | ≤ 0.06 |
Physical Properties
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7,850 kg/m³ | 0.284 lb/in³ |
| Melting Point | 1,510°C | 2,750°F |
| Thermal Conductivity | 36.0 W/m·K | 250 BTU·in/ft²·h·°F |
| Electrical Conductivity | 1.72 × 10^6 S/m | 1.00 × 10^6 S/m |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 490 J/kg·K | 0.117 BTU/lb·°F |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 11.7 × 10^-6 /°C | 6.5 × 10^-6 /°F |
| Electrical Resistivity | 5.81 × 10^-7 Ω·m | 5.81 × 10^-7 Ω·m |
Mechanical Properties
AC (Air Cooled) Sate
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 570 MPa | 82.7 ksi |
| Yield Strength | 485 MPa | 70.3 ksi |
| Brinell Hardness | 190 HB | 190 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | 80 HRB | 80 HRB |
| Vickers Hardness | 210 HV | 210 HV |
| Elongation | 20% | 20% |
| Elastic Modulus | 200 GPa | 29 msi |
QT (Quenched & Tempered) State
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 690 – 760 MPa | 100 – 110.2 ksi |
| Yield Strength | 600 – 700 MPa | 87 – 101.5 ksi |
| Elongation | 15 – 20% | 15 – 20% |
| Reduction of Area | 50 – 60% | 50 – 60% |
| Impact Absorption Energy | 200 – 250 J (at -20°C) | 147 – 184 ft-lb (at -4°F) |
| Elastic Modulus | 200 GPa | 29 msi |
Industries & Applications
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Pipelines, Drill Pipes, Line Pipes, Casings |
| Construction | Structural Beams, Girders, Columns, Bridge Components |
| Automotive | Chassis Frames, Suspension Arms, Axle Housings, Roll Cages |
| Shipbuilding | Hull Structures, Bulkheads, Deck Plates, Rudders |
| Pressure Vessels | Pressure Tanks, Heat Exchangers, Reactor Vessels, Boiler Drums |
| Energy & Power Generation | Wind Turbine Towers, Gas Transmission Lines, Power Plant Piping, Structural Supports |
| Heavy Equipment | Excavator Booms, Crane Jibs, Loader Arms, Bulldozer Blades |
| Mining | Conveyor Systems, Support Beams, Crushing Equipment, Shovels |
Machining
Heat Treatment
- Austenitizing: Heat the steel to 880°C – 950°C to form austenite.
- Quenching: Rapidly cool to transform austenite into martensite, increasing hardness.
- Tempering: Heat to 500°C – 700°C to reduce brittleness and improve toughness.
- Cooling: Let the steel cool in the air to complete the process.
Surface Finish
- Pickling: Removes surface oxides and scales using acid.
- Shot Blasting: Cleans the surface by blasting with abrasive materials.
- Grinding: Smooths the surface using abrasive wheels.
- Polishing: Further smooths and enhances the shine of the surface.
- Coating: Applies a protective layer, such as paint or zinc, to prevent corrosion.
- Passivation: Enhances corrosion resistance by forming a protective oxide layer.
*Customization is available upon request.
Disclaimer
The provided heat treatment and surface treatment processes are general guidelines. Actual conditions may vary depending on specific applications and requirements. It is recommended to consult with a professional metallurgist or material scientist to tailor the processes to your particular needs. The information herein is not a substitute for professional advice and should not be relied upon as such.
Our Service
SteelPRO Group – manufacturer and solution provider for special steel, offering multi-industry application solutions and customised services, 100% quality free, accompanying customers in their growth!
Our Quality Control
- Roundness
- Tolerance
- Microstructure
- Non-Destructive Testing
- Destructive Testing
- Process Control
Service Integration Processing
- Welding
- Metal Fabrication
- CNC Machining
- Lathe
- Forming
QUESTION 1
QUESTION 2
QUESTION 3
QUESTION 4
QUESTION 4
CONTACT
CONTACT
Certifications






Other Products
-

-

SteelPRO Group offers FH550 high-strength structural steel plates for shipbuilding....
-

SteelPRO Group offers DH550 high-strength shipbuilding steel plates in stock....
-

SteelPro Group offers FH36 high-strength steel for shipbuilding. It has...
















