Low Carbon Steel
Versatile Performance. Affordable Strength. Enhance Projects with Reliable Low Carbon Steel.
Introduction to Low Carbon Steel
Low carbon steel (LC Steel), or mild steel, contains approximately 0.05% to 0.25% carbon by weight. It has a yield point of around 250 MPa, a density of 7.85 g/cm³, and a Young’s modulus of about 210 GPa. Due to its low cost and acceptable mechanical properties, low carbon steel is commonly used in various industries. Unlike Medium Carbon Steel and High Carbon Steel, which offers greater hardness and strength, low carbon steel is less ductile but easier to weld and form.
Low-carbon steel is highly popular due to its excellent weldability and ductility. Commonly used in structural applications, automotive manufacturing, and wire products, its lower carbon content provides a balance of strength and flexibility. Unlike medium and high carbon steel, which have higher tensile strength and hardness but are less ductile, low carbon steel can be alloyed and heat-treated to improve strength and hardness. Its low cost and versatile mechanical properties make it a preferred choice for many applications.

Benefits of Low Carbon Steel
- Low carbon steel offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive choice for various industrial applications:
- Cost-Effective: The price is relatively low, making it a budget-friendly option for many industries.
- High Ductility: Low carbon steel is ductile, allowing it to be easily formed and shaped without cracking.
- Good Weldability: Its low carbon content improves weldability, making it easier to join pieces together.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, from structural steel to wire products. Unlike medium carbon steel, low carbon steel includes properties that enhance its flexibility.
- Machinability: Easier to machine compared to higher carbon steels, reducing manufacturing costs.
- Corrosion Resistance: While not as corrosion-resistant as stainless steel, low carbon steel can be treated to improve its resistance.
- High Strength and Toughness: With proper heat treatment, low carbon steel can achieve improved strength and toughness, making it suitable for demanding applications.

Types of Low Carbon Steel
- Low carbon steel, also known as mild steel, is a type of steel that contains a low amount of carbon. This results in various types tailored to specific needs and applications. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right material for the intended use:
- Low Carbon Steel Sheet: Used in automotive and appliance manufacturing, offering flexibility and ease of fabrication.
- Low Carbon Steel Bars: Commonly used in construction for reinforcing concrete structures and producing machinery parts.
- Low Carbon Steel Plates: Utilized in shipbuilding, heavy machinery, and construction for creating durable, large structures.
- Low Carbon Steel Coil: Used in a wide variety of applications, including metal roofing and structural components, due to its uniform thickness and formability.
- Low Carbon Steel Wire: Used for making wire products like nails, mesh, and fencing, known for its ductility and ease of use.
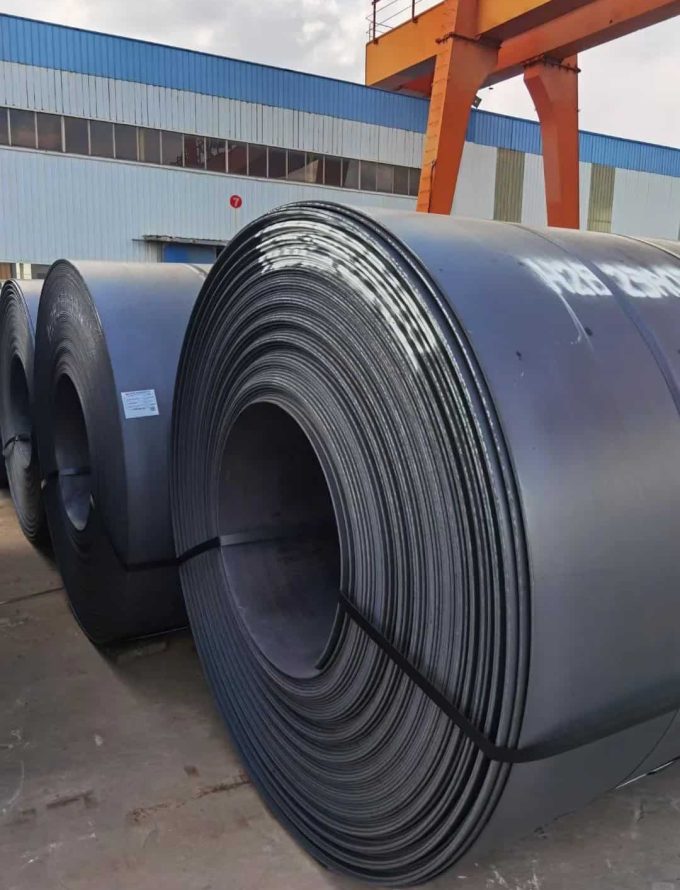
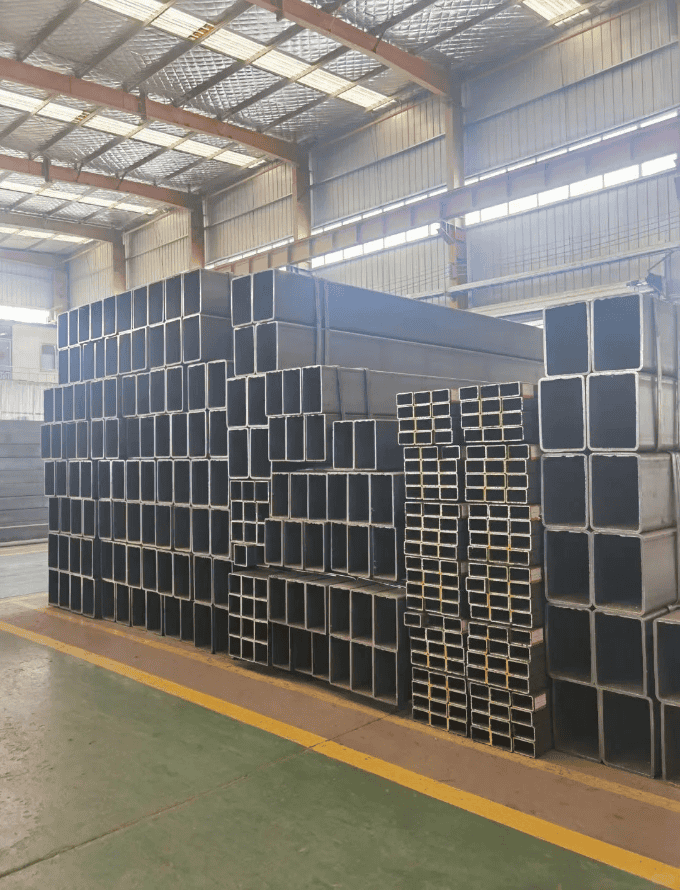




Industries & Applications
Some common industries and applications include:
Construction
Automotive
Wire Products
Machinery
Pipes and Tubes
Furniture
Dimensions & Properties
| Grade 42 | ASTM A36 | 1020 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength | 290 MPa (42 ksi) | 250 MPa (36 ksi) | 290 MPa (42 ksi) |
| Tensile Strength | 415 MPa (60 ksi) | 400-550 MPa (58-80 ksi) | 410-550 MPa (60-80 ksi) |
| Material Standard | ASTM A572 / A572M | ASTM A36 | SAE/AISI 1020 |
| Vickers Hardness | 130-170 HV | 100-140 HV | 130-160 HV |
Low Carbon Steel When & Where You Need It
Here, you get more than just quality steel. With multiple facilities across the country capable of providing high-strength steels, we can also work with you to manage your inventory, ensuring you get product when and where you need it to keep your production running.
Explore Our Available Steel Products & Grades
Our knowledge and experience give nearly 100% accurate delivery of High Carbon, Low Carbon, Stainless Steel products processed and packaged to your exact specifications.
Does low-carbon steel crack?
Low-carbon steel is less likely to crack due to its higher ductility and toughness.
When not to use carbon steel?
Avoid using carbon steel in highly corrosive environments or where high temperatures are involved.
Can you prevent carbon steel from rusting?
Yes, you can prevent rusting by applying coatings, using rust inhibitors, or through galvanization.
What is the difference between mild steel and medium and high carbon steel?
Mild steel has a lower carbon content, making it more ductile and easier to weld and shape, whereas medium and high carbon steels have higher carbon content, providing greater hardness and strength but making them less ductile and more difficult to weld.
How does your low carbon steel perform in terms of weldability and machinability?
Our low carbon steel offers excellent weldability and machinability due to its low carbon content and balanced properties.















