Introduction to High Strength Structural Steel
Benefits of High Strength Structural Steel
Types of High Strength Structural Steel
Shapes of High Strength Structural Steel
Introduction to High Strength Structural Steel
Processing techniques like hot-rolling, cold-rolling, press hardening, and post-forming heat treatments improve both mechanical properties and shape complexity. HSSS is vital for load-bearing structures and plays key roles in automotive, aerospace, energy, and construction industries. Its benefits—such as weight reduction, impact resistance, and durability—make it ideal for high-performance machinery, safety components, and infrastructure projects.

Benefits of High Strength Structural Steel
High Strength Structural Steel (HSSS) solves key industry challenges by offering lighter, stronger, and more durable solutions, optimizing production efficiency, structural performance, and sustainability.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Reduces material usage, permanent loads, and transportation costs without sacrificing performance.
- Durability and Reliability: Offers excellent fatigue, corrosion, and seismic resistance for long-lasting, high-performance applications.
- Weldability and Design Flexibility: Supports advanced designs through efficient welding, hot-rolling, cold-rolling, and press hardening processes.
- Enhanced Space Utilization: Enables slimmer, lighter structures, optimizing space and design efficiency.
- Cost and Efficiency Gains: Lowers production and assembly costs with fewer components, while improving fuel efficiency and reducing wear in vehicles.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reduces carbon emissions, conserves energy, and supports recyclability, promoting a circular economy.


Types of High Strength Structural Steel
- High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel (HSLA):
- Grades: ASTM A572, A588, S355
- Lightweight with high weldability and corrosion resistance, used in bridges, buildings, and machinery.
- Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS):
- Grades: DP (DP500), TRIP (TRIP690), CP (CP800), Martensitic (MS1200)
- Combines phases for ductility and tensile strength, key for automotive safety and lightweight components.
- Ultra-High Strength Steel (UHSS):
These types meet industry demands by offering durability, reduced weight, corrosion resistance, and cost-effective performance across sectors like infrastructure, transportation, and heavy equipment.


Shapes of High Strength Structural Steel
- Plates and Sheets: Flat steel products for bridges, shipbuilding, and machinery.
- Beams (I, H, T): Structural members for buildings, bridges, and industrial frameworks.
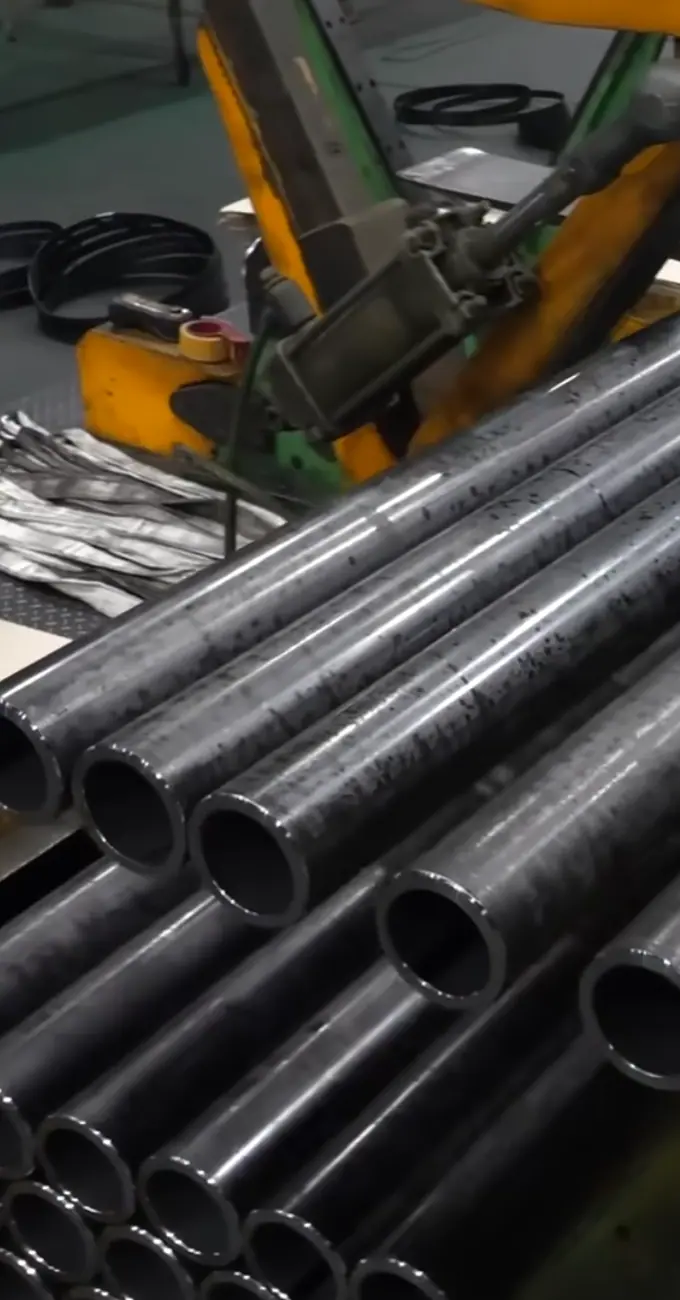
- Pipes and Tubes: Hollow sections used in pipelines, automotive exhausts, and frameworks.
- Bars and Rods: Reinforcement (rebar) and mechanical components like shafts and fasteners.
- Angles and Channels: L- or C-shaped members for bracing structures and equipment supports.
- Flat Bars and Strips: Precision parts for automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
- Wires: Steel strands for cables, reinforcement, and fencing.
These shapes meet diverse industrial needs, balancing strength, flexibility, and weight efficiency.



Industries & Applications
Some common industries and applications include:
Construction

Automotive

Aerospace

Energy
Shipbuilding

Railways
Heavy Machinery

Infrastructure
High Strength Structural Steel Physical Properties
High Strength Structural Steel (HSSS) is recognized for its exceptional physical properties, making it vital in engineering applications.
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7850 kg/m³ | 490 lb/ft³ |
| Melting Point | 1425 - 1540 °C | 2600 - 2800 °F |
| Boiling Point | 2900 °C | 5250 °F |
| Thermal Conductivity | 45 W/(m·K) | 31 BTU/(hr·ft²·°F) |
| Electrical Conductivity | 1.5 x 10⁶ S/m | 1.5 x 10⁶ S/m |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 500 J/(kg·K) | 0.12 BTU/(lb·°F) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 11 x 10⁻⁶ /K | 6.1 x 10⁻⁶ /°F |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.000001 Ω·m | 0.000001 Ω·m |
High Strength Structural Steel Specifications
| Grade | Specifications(mm) | Standard | ||
| Thickness | Width | Length | ||
| Q355B | 6~320 | 900~4800 | 3000~25000 | GB/T 1591 |
| Q355C/D | 6~120 | |||
| Q355NB/C/D | 6~250 | |||
| Q355NE | 6~200 | |||
| Q390NB/C/D/E | 6~150 | |||
| Q420NB/C/D/E | ||||
| Q550C/D/E | ||||
| A678 Gr.A | 6~40 | ASTM A678/A678M | ||
| A678 Gr.B | 6~65 | |||
| A678 Gr.C | 6~50 | |||
| A678 Gr.D | 6~75 | |||
| S355JR/J0 | 6~300 | EN 10025-2 | ||
| S355J2/K2 | ||||
| S355N/NL | 6~250 | EN 10025-3 | ||
| S420N/NL | ||||
| S460N/NL | 6~200 | |||
| S355M/ML | 6~120 | EN 10025-4 | ||
| S420M/ML | ||||
| S460M/ML | ||||
| S460Q/QL1/QL2 | 6~150 | EN 10025-6 | ||
| S500Q/QL1/QL2 | ||||
| SS540 | 6~40 | JIS G 3101 | ||
| SM520B/C | JIS G 3106 | |||
Related Grades
Find More High Strength Structural Stainless Steel Grades at SteelPRO Group!
A514 quenched and tempered alloy steel offers exceptional strength and weldability, suitable for heavy construction and high-performance machinery.
S500 high-strength steel provides a balance of toughness and lightweight properties, ideal for demanding load-bearing applications.
S355 low-alloy steel delivers versatility, strength, and corrosion resistance, widely used across various industries.
Q550 high-yield steel, produced under Chinese standards, performs well under extreme loads in heavy machinery and bridge construction.
S460 fine-grain structural steel offers excellent strength and ductility, commonly applied in energy infrastructure and large frameworks.
A678 high-strength steel ensures superior atmospheric corrosion resistance, frequently used for bridges and outdoor structures.
High Strength Structural Steels When & Where You Need It
At SteelPRO Group, you get more than just quality steel. With multiple facilities across the country capable of providing high-strength steels, we can also work with you to manage your inventory, ensuring you get product when and where you need it to keep your production running.
Explore Our Available Steel Products & Grades
Our knowledge and experience give nearly 100% accurate delivery of High Carbon, Low Carbon, Stainless Steel products processed and packaged to your exact specifications.
What is high strength structural steel?
High Strength Structural Steel (HSSS) is a type of steel designed for enhanced yield and tensile strength, making it suitable for demanding structural applications.
What is high yield strength structural steel?
High yield strength structural steel refers to steel grades with yield strengths greater than 250 MPa, ideal for applications requiring resistance to deformation.
What are the grades of high-strength steel?
Common grades include ASTM A572, A992, S355, and various Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS) grades like DP and TRIP.
What is the difference between high strength steel and normal steel?
High strength steel has superior mechanical properties, allowing it to support heavier loads and resist deformation better than normal steel.
How do the costs of HSSS compare with other materials, and what factors influence pricing?
Analyzing the total cost of ownership, including initial costs, fabrication, and lifecycle expenses, helps in making informed purchasing decisions.















