STRUCTURAL STEEL
Stronger Structures. Lighter Build. Enhance Your Projects with Superior Structural Materials.
Introduction to Structural Steel
Benefits of Structural Steel
Types of Structural Steel
Industries & Applications
What is Structural Steel
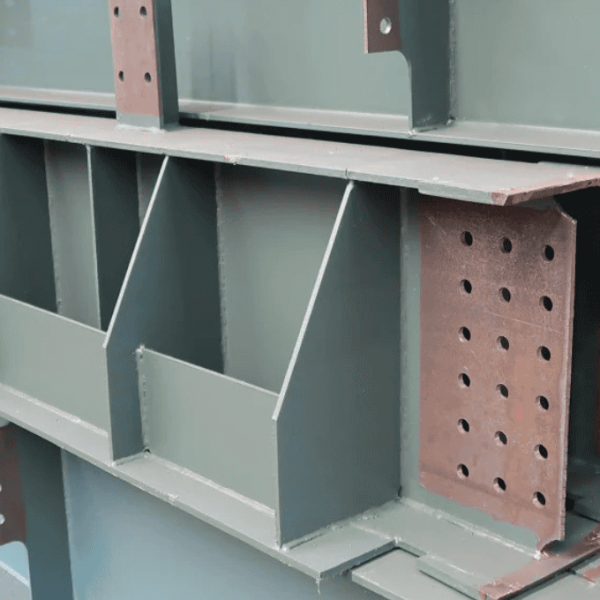
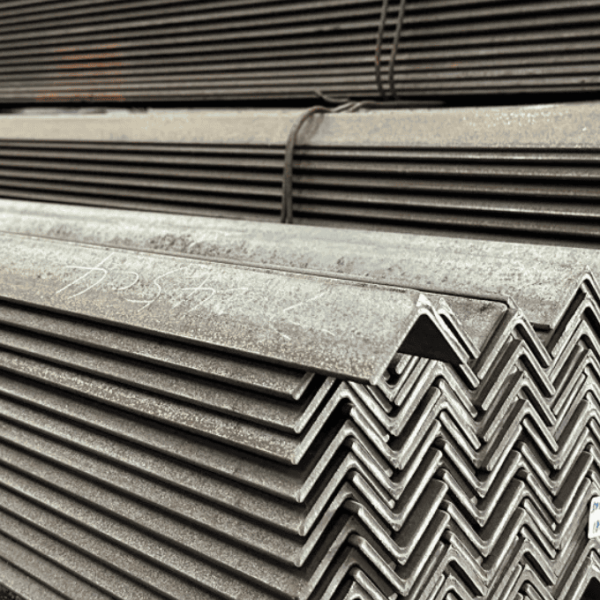


Benefits of Structural Steel
- Our structural steel offers numerous advantages that make it an ideal choice for construction projects:
- Versatility: Fabricates into various shapes and sizes.
- Durability: High strength-to-weight ratio and tensile strength.
- Safety: Meets regulations and resists mold and termites.
- Easy Assembly: Quick on-site construction.
- Cost-Effective: Lowers foundation costs and speeds up building.
- Fire and Water Resistance: Coatings enhance protection.
- Recyclability: Highly recyclable, reducing environmental impact.
- Long Lifespan: Lasts 50 to 100 years with maintenance.
- Adaptability: Easy to modify and renovate.
- Environmental Resistance: Performs well in extreme conditions.
Types of Structural Steel
- 1. Beams
- I-Beams: I-shaped in cross-section, commonly used in major structures for support.
- U-Beams: U-shaped, used for supporting various loads.
- Round or Square Beams: Solid beams are found more in industrial equipment and appliances.
2. Angles- Angled Beams: L-shaped beams with two legs at a 90-degree angle, used for anchoring floor systems and angular connections.
- Hollow Structural Sections (HSS): Circular steel bars with a hollow cross-section are used in welded steel frames for multi-directional loading.
3. Plates- Flat Bars: Rectangular flat pieces are used as connective members in residential and commercial framing.
4. Channels- C-Channels: Hot-rolled into a C-shape, used for supporting main load-bearing beams.
5. Rebar- Reinforcement Steel: Laid within the concrete to provide additional strength, used in bridges, buildings, skyscrapers, homes, warehouses, and foundations.

Industries & Applications
Structural steel can be used in a variety of industries and applications, as it is a very versatile and commonly used form of steel.
Some common industries and applications include:
Construction
Infrastructure
Storage Tanks
Tools and Machinery
Household Appliances
Food and Beverage Packaging
Dimensions & Properties
| Q235 | Q345 | Q390 | Q420 | Q500q | Q600q | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Ordinary Structural Steel | Ordinary Structural Steel | High-rise Building Steel | High-rise Building Steel | Bridge Steel | Bridge Steel |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 235 | 345 | 390 | 420 | 500 | 600 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 370-500 | 470-660 | 510-660 | 550-720 | 630-780 | 690-850 |
| Standard | GB/T 700 | GB/T 1591 | GB/T 1591 | GB/T 1591 | GB/T 714 | GB/T 714 |
| Vickers Hardness (HV) | 120-140 | 140-200 | 160-220 | 170-230 | 200-260 | 230-290 |
Structural Steels When & Where You Need It
Here, you get more than just quality steel. With multiple facilities across the country capable of providing high-strength steels, we can also work with you to manage your inventory, ensuring you get product when and where you need it to keep your production running.
Explore Our Available Steel Products & Grades
Our knowledge and experience give nearly 100% accurate delivery of High Carbon, Low Carbon, Stainless Steel products processed and packaged to your exact specifications.
What is the steel grade of steel, and how does it affect the steel used?
The steel grade indicates the quality level of the steel, reflecting its chemical composition and mechanical properties. Different grades are used for various construction and engineering applications to ensure the steel has adequate strength and durability under specific conditions.
What are the key mechanical properties of structural steel?
The key mechanical properties of structural steel include tensile strength, yield strength, ductility, and toughness. These properties determine how the steel performs under different loads and stresses.
How does the tensile strength of structural steel influence its performance in construction?
Tensile strength is the maximum stress that structural steel can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. Higher tensile strength ensures the steel structure can bear greater loads without failure, making it crucial for construction stability.
What is the role of yield strength in the selection of structural steel?
Yield strength is the stress at which structural steel begins to deform plastically. It is important to determine the load-carrying capacity of the steel without permanent deformation. Selecting steel with appropriate yield strength ensures safety and structural integrity.
How does the chemical composition of structural steel affect its mechanical properties?
The chemical composition of structural steel, including elements like carbon, manganese, and silicon, significantly influences its mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility. Proper balance in the chemical composition ensures the steel meets specific performance requirements for various applications.















