A678 | High Strength Structural Steel
A678 | High Strength Structural Steel
A678 is a high-strength, low-alloy structural steel. The “A” follows ASTM standards, with grades (A, B, C, D) indicating mechanical differences. Equivalent grades include EN S355JR and GB Q345B. It offers high tensile strength, toughness, and weldability, making it ideal for bridges, pressure vessels, and construction equipment.
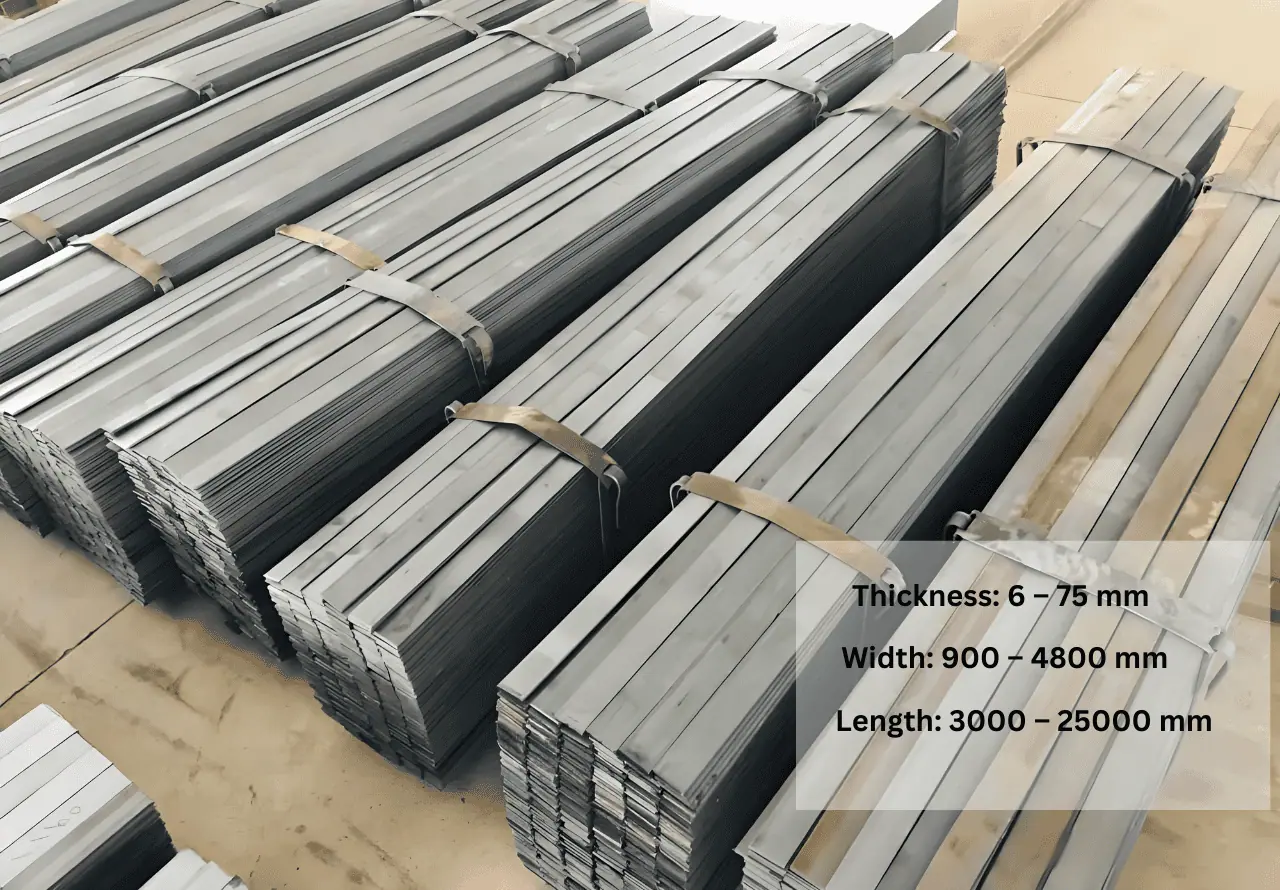
According to ASTM A678/A678M, we offer products in grades A to D with thicknesses ranging from 6 to 75 mm, 900~4800 mm width, and 3000~25000 mm length to ensure versatility for various structural applications.
Description
What is A678 Steel
Characteristics of A678 Steel
Chemical Compositions
| Element | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon, C | ≤ 0.16 – 0.22 |
| Manganese, Mn | 1.00 – 1.60 |
| Silicon, Si | 0.15 – 0.50 |
| Phosphorus, P | ≤ 0.035 |
| Sulfur, S | ≤ 0.040 |
| Copper, Cu | 0.20 – 0.35 |
| Nickel, Ni | ≤ 0.25 |
| Chromium, Cr | ≤ 0.25 |
| Molybdenum, Mo | ≤ 0.08 |
| Vanadium, V | ≤ 0.11 |
Physical Properties
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.85 g/cm³ | 0.284 lb/in³ |
| Melting Point | 1450 – 1520 °C | 2642 – 2768 °F |
| Boiling Point | ~3000 °C | ~5432 °F |
| Thermal Conductivity | 45 – 50 W/(m·K) | 26 – 29 BTU·in/(h·ft²·°F) |
| Electrical Conductivity | 6.99 MS/m | 6.99 MS/m |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 486 J/(kg·K) | 0.116 BTU/(lb·°F) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 11.5 × 10⁻⁶ /K | 6.4 × 10⁻⁶ /°F |
| Electrical Resistivity | 14 × 10⁻⁸ Ω·m | 14 × 10⁻⁸ Ω·m |
Mechanical Properties
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 490 – 850 MPa | 71,000 – 123,000 psi |
| Yield Strength | 314 – 793 MPa | 46,000 – 115,000 psi |
| Brinell Hardness | 170 – 321 HB | 170 – 321 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | 84 – 95 HRB | 84 – 95 HRB |
| Vickers Hardness | 180 – 340 HV | 180 – 340 HV |
| Elongation | 12 – 33% | 12 – 33% |
| Elastic Modulus | 200 – 210 GPa | 29,000 – 30,500 ksi |
Data After QT(Quenching and Tempering) Processing
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 650 – 780 MPa | 94,000 – 113,000 psi |
| Yield Strength | 520 – 600 MPa | 75,000 – 87,000 psi |
| Brinell Hardness | 220 – 280 HB | 220 – 280 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | HRC 40 – 45 | HRC 40 – 45 |
| Vickers Hardness | 210 – 260 HV | 210 – 260 HV |
| Elongation | 15 – 18% | 15 – 18% |
| Elastic Modulus | 210 GPa | 30,500,000 psi |
Industries & Applications
| Industries | Products |
|---|---|
| Construction | Beams, Columns, Frames, Reinforcements, Plates |
| Bridges | Bridge Decks, Trusses, Girders, Supports, Barriers |
| Pressure Vessels | Tanks, Boilers, Heat Exchangers, Cylinders, Pipes |
| Heavy Machinery | Crane Arms, Excavator Buckets, Chassis, Tools, Lifting Equipment |
| Energy | Wind Turbine Towers, Pipelines, Offshore Structures, Supports, Frames |
| Shipbuilding | Hull Structures, Bulkheads, Deck Plates, Frames, Fuel Tanks |
| Mining | Conveyor Systems, Mining Trucks, Drilling Rigs, Support Beams, Structural Platforms |
| Railway | Rail Tracks, Bridge Structures, Rolling Stock, Support Columns, Switchgear |
Machining
A678 Steel Heat Treatment
- Heating: Heat the steel to 850–900°C (1560–1650°F) to achieve uniform austenitization.
- Soaking: Hold the steel at the target temperature for 1–2 hours, depending on thickness, to ensure even heating throughout.
- Quenching: Rapidly cool in water or oil to harden the steel and enhance strength.
- Tempering: Reheat to 540–680°C (1000–1255°F) for 1–2 hours to reduce brittleness and improve toughness.
- Cooling: Allow the steel to cool slowly in air to stabilize the microstructure.
A678 Surface Finish
- Galvanizing: Coats the steel with zinc to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Painting: Adds a protective layer and improves appearance for outdoor use.
- Powder Coating: Provides a durable, decorative finish resistant to chipping and fading.
- Shot Blasting: Cleans the surface and improves adhesion for subsequent coatings.
- Pickling: Removes scale, rust, and oxides to prepare the surface for further treatment.
- Anodizing: Enhances surface hardness and corrosion resistance (less common for steel).
- Electroplating: Applies a metal layer (such as chrome or nickel) to improve wear and corrosion resistance.
Our Service
SteelPRO Group – manufacturer and solution provider for special steel, offering multi-industry application solutions and customised services, 100% quality free, accompanying customers in their growth!
Our Quality Control
- Roundness
- Tolerance
- Microstructure
- Non-Destructive Testing
- Destructive Testing
- Process Control
Service Integration Processing
- Welding
- Metal Fabrication
- CNC Machining
- Lathe
- Forming
QUESTION 1
QUESTION 2
QUESTION 3
QUESTION 4
QUESTION 4
CONTACT
CONTACT
Certifications






Other Products
-

-

SteelPRO Group offers FH550 high-strength structural steel plates for shipbuilding....
-

SteelPRO Group offers DH550 high-strength shipbuilding steel plates in stock....
-

SteelPro Group offers FH36 high-strength steel for shipbuilding. It has...

















