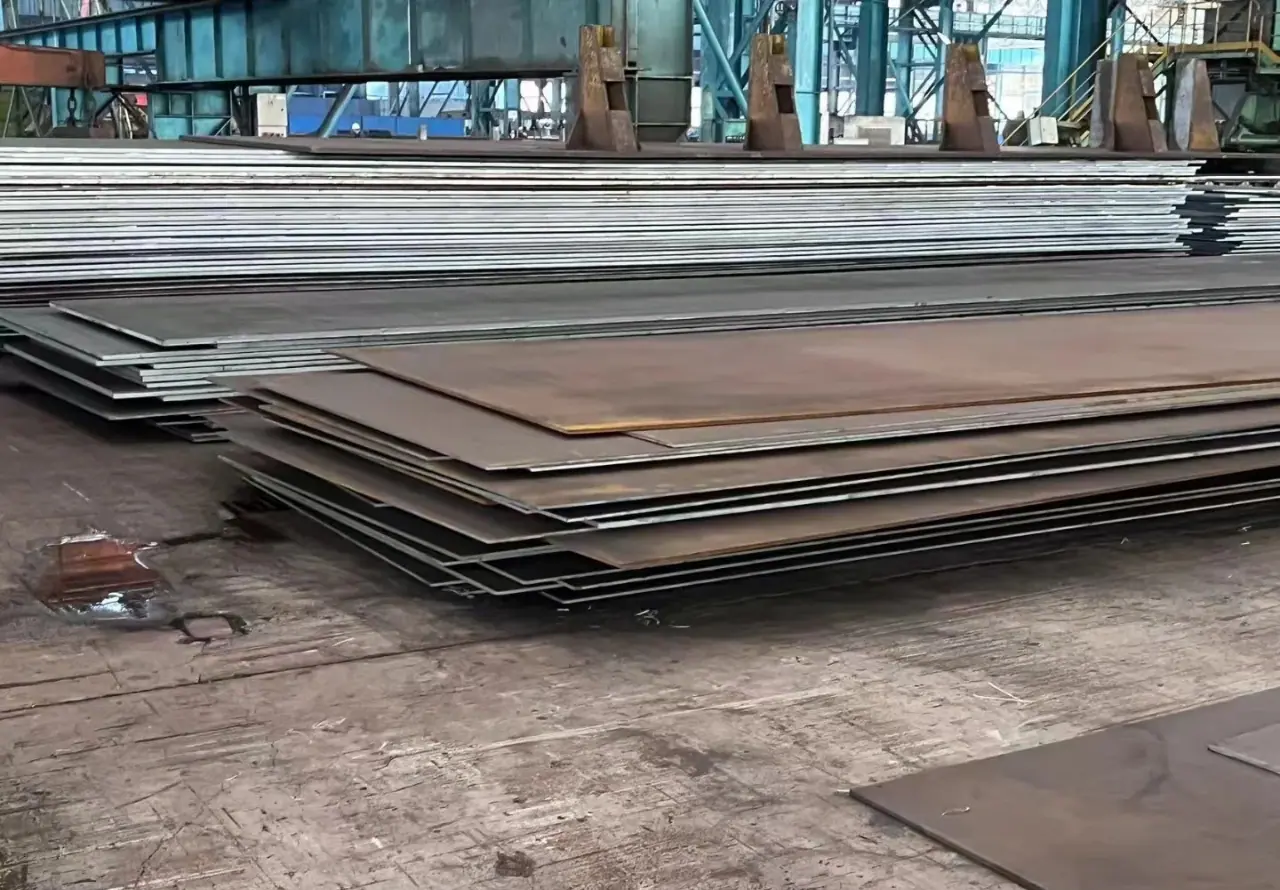
NM400 | AR400 | Hardox 400 Wear-Resistant Steel
NM400 | AR400 | Hardox 400 Wear-Resistant Steel
NM400 is a high-strength wear-resistant steel used widely in heavy industries. The “NM” stands for “wear-resistant,” and “400” indicates its average Brinell hardness. Known for its excellent hardness and toughness, NM400 has superior abrasion resistance. It is typically hot-rolled and used in mining, construction, and manufacturing. Common applications include dump truck bodies, crusher parts, and cutting edges.
Description
What is NM400?
NM400 is a wear-resistant steel plate composed of about 90% iron, 0.35% carbon, and alloying elements like chromium, manganese, and silicon. It is a solid material processed through hot rolling, known for its hardness and toughness. NM400 is used in mining, construction, and manufacturing for applications such as dump truck bodies, crusher parts, and cutting edges. It offers excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for high-wear environments. NM400 can be classified by thickness and hardness, offering options for heavy-duty applications.Characteristics of NM400?
NM400 is a high-strength, wear-resistant steel known for its excellent hardness and toughness. Its providing superior abrasion resistance. This makes NM400 ideal for use in environments with heavy wear and tear. The primary advantage of NM400 is its durability, which reduces the frequency of part replacements and maintenance costs for customers. Its excellent wear resistance extends the lifespan of equipment, making it a cost-effective choice for industries such as mining, construction, and manufacturing. However, NM400’s high hardness can make it challenging to machine and weld. For applications requiring easier machinability or better weldability, steels like Q235 Steel or other mild steels can be used as alternatives or in conjunction with NM400 to balance the need for both wear resistance and ease of processing.Chemical Compositions
| Element | Max Percentage |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.30% max |
| Manganese (Mn) | 1.20% max |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.70% max |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.025% max |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.010% max |
| Chromium (Cr) | 1.40% max |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.60% max |
| Nickel (Ni) | 0.50% max |
| Boron (B) | 0.004% max |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance |
Physical Properties
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.85 g/cm³ | 0.284 lb/in³ |
| Melting Point | 1425-1460°C | 2597-2660°F |
| Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available |
| Thermal Conductivity | 15-25 W/m·K | 8.7-14.5 BTU·ft/h·°F |
| Electrical Conductivity | Not Available | Not Available |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.46 J/g·K | 0.11 BTU/lb·°F |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 12.2 µm/m·K | 6.8 µin/in·°F |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.55 µΩ·m | 0.55 µΩ·m |
Mechanical Properties
AC Properties of NM400
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 1250 MPa | ≥ 181 ksi |
| Yield Strength | ≥ 1000 MPa | ≥ 145 ksi |
| Brinell Hardness | ≥ 370 HB | ≥ 370 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | ≥ 40 HRC | ≥ 40 HRC |
| Vickers Hardness | ≥ 340 HV | ≥ 340 HV |
| Elongation | ≥ 10% | ≥ 10% |
| Elastic Modulus | 210 GPa | 30.5 Msi |
QT Properties of NM400
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (Rm) | ≥ 1250 MPa | ≥ 181 ksi |
| Yield Strength (Rp0.2) | ≥ 1000 MPa | ≥ 145 ksi |
| Impact Toughness (KV/Ku) | ≥ 24 J | ≥ 17.7 ft-lb |
| Elongation (A) | ≥ 10% | ≥ 10% |
| Reduction in Area (Z) | ≥ 40% | ≥ 40% |
| Brinell Hardness (HBW) | ≥ 370 HBW | ≥ 370 HBW |
The Tensile Strength, Yield Strength, and Brinell Hardness of NM400 remain unchanged after QT treatment as they are already optimized; QT mainly enhances toughness and ductility.
Industries & Applications
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Mining Industry | Used in dump truck liners, excavator buckets, crusher plates, and wear-resistant linings. |
| Construction Machinery | Ideal for bulldozer blades, loader shovels, and other heavy-duty equipment parts. |
| Agriculture | Applied in plowshares, tillage tools, and other agricultural machinery components. |
| Cement Industry | Utilized in chutes, hoppers, and conveyor systems. |
| Recycling Industry | Used in shredders, crushers, and other wear-intensive equipment. |
| Steel Manufacturing | Employed in rolling mills and other equipment requiring high wear resistance. |
| Transportation | Applied in the construction of industrial vehicles and heavy transport equipment. |
Machining
NM400 Heat Treatment
- Solution Treatment: Heat to 1050-1100°C, hold, then rapidly cool (usually in water).
- Aging Treatment: Heat at 200-500°C for an extended period.
- Quenching: Heat to 900-1000°C, then rapidly cool.
- Tempering: Reheat quenched steel to 200-600°C, then cool.
- Normalizing: Heat to 850-950°C, then air cool.
- Annealing: Heat to 700-800°C, hold, then slowly cool.
NM400 Surface Finish
- Surface Hardening: Includes flame and induction hardening.
- Carburizing: Heat in a carbon-rich environment at high temperature.
- Nitriding: Heat in a nitrogen or ammonia atmosphere.
- Carbonitriding: Similar to carburizing but with nitrogen addition.
- Electroplating: Electrochemically deposit a metal layer (e.g., chromium, nickel).
- Thermal Spraying: Apply a high-hardness, wear-resistant coating.
Custom surface treatment requirements can be accommodated upon request.
Disclaimer
The above heat treatment instructions and surface finish processing methods for NM400 are provided for informational purposes only. Actual results may vary based on the specific conditions and equipment used. It is recommended to perform testing and consult with a metallurgical expert or the material supplier to ensure the processes are suitable for your specific application. The user assumes all risks and liability for the use of this information.
Our Service
SteelPRO Group – manufacturer and solution provider for special steel, offering multi-industry application solutions and customised services, 100% quality free, accompanying customers in their growth!
Our Quality Control
- Roundness
- Tolerance
- Microstructure
- Non-Destructive Testing
- Destructive Testing
- Process Control
Service Integration Processing
- Welding
- Metal Fabrication
- CNC Machining
- Lathe
- Forming
QUESTION 1
QUESTION 2
QUESTION 3
QUESTION 4
QUESTION 4
CONTACT
CONTACT
Certifications






Other Products
-

-

SteelPRO Group offers FH550 high-strength structural steel plates for shipbuilding....
-

SteelPRO Group offers DH550 high-strength shipbuilding steel plates in stock....
-

SteelPro Group offers FH36 high-strength steel for shipbuilding. It has...
















