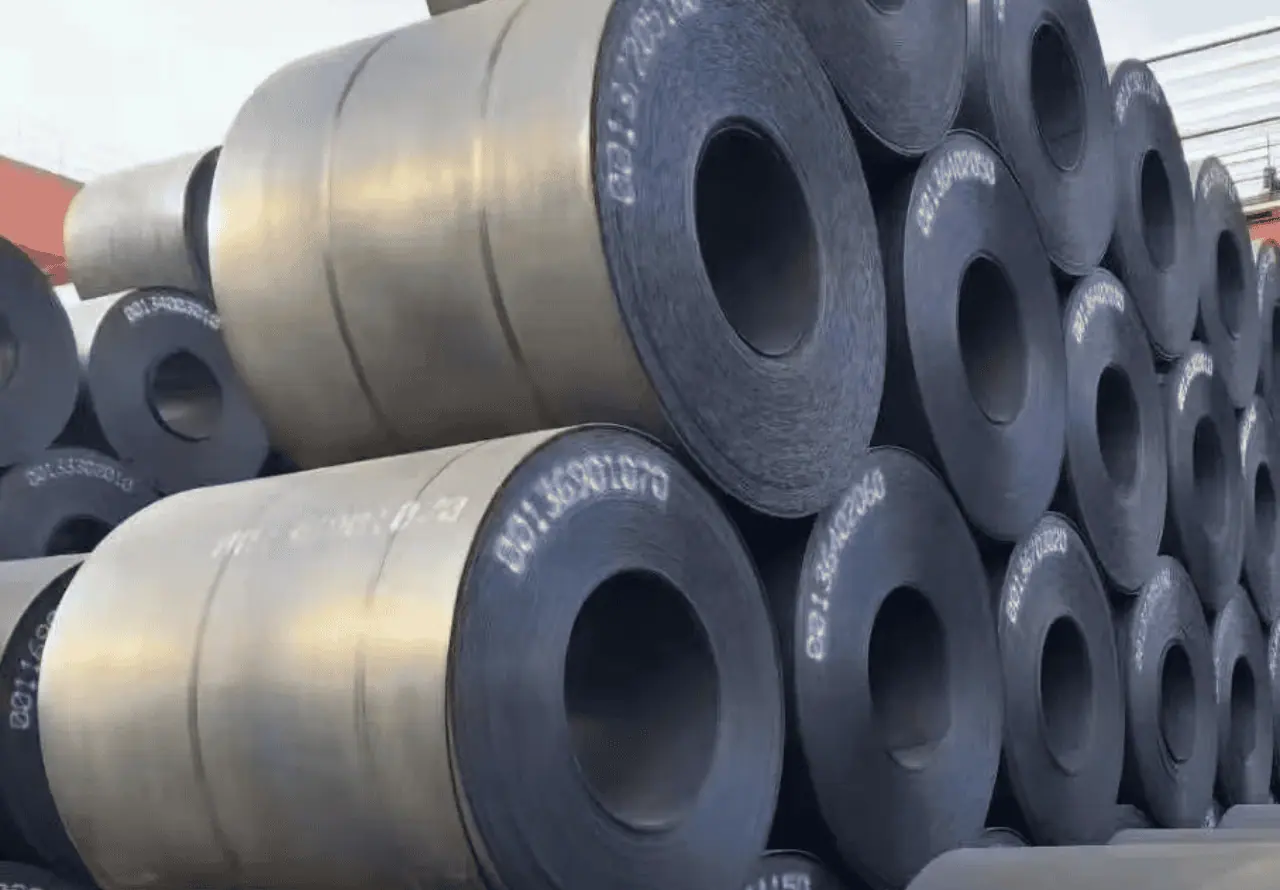
DH36 | HSLA Steel Shipbuilding Steel
DH36 | HSLA Steel Shipbuilding Steel
DH36 is a high-strength structural steel used mainly in shipbuilding. It conforms to the ASTM A131/A131M standard. The “DH” denotes the grade, where “D” stands for high-strength and “H” indicates heat treatment. Equivalent grades include ABS DH36, LR DH36, and BV DH36. DH36 steel features high yield strength, good toughness, and excellent weldability. It is primarily used in ship hull construction, offshore structures, and marine engineering projects.
We provide DH36 plates and profiles with tight dimensional control, compliant with recognized standards and certifications.
Description
What Is DH36?
DH36 is a high-strength structural steel primarily used in shipbuilding. It consists of approximately 98% iron and 2% carbon and alloying elements. This steel is characterized by its solid form and is typically dark grey in color. Key properties include high yield strength, good toughness, and excellent weldability. DH36 is commonly used in the construction of ship hulls, offshore structures, and marine engineering projects. It is produced through the hot-rolling process and falls under the category of high-strength, low-alloy steel.Characteristics of DH36
DH36 steel offers high tensile strength and excellent toughness. It has good weldability, allowing for easy fabrication. The steel’s resilience in harsh marine environments makes it ideal for shipbuilding. It is also resistant to corrosion, enhancing its durability. DH36 is commonly used in constructing ship hulls and offshore structures. For applications requiring even higher strength or specific properties, consider steel grades like AH36, EH36, or FH36. These alternatives provide variations in strength and toughness to meet diverse engineering needs.DH36 Steel Manufacturer
Our DH36 galvanized steel products are specifically engineered to meet the rigorous demands of high-strength structural applications in the shipbuilding industry, ensuring reliable performance and safety:
-
- Standard: ASTM A131
- Certificate: EN 10204 Type 3.2
- Impact Strength: 25 ft-lbs at -4°F (34 J at -20°C)
We supply DH36 plates in thicknesses ranging from 6 mm to 100 mm, with the capability to provide plates up to 150 mm thick for specialized applications such as icebreakers and offshore structures. We have extensive experience supplying DH36 steel for various vessels, including bulk carriers, container ships, tankers, and LNG carriers.
Classifications

Chemical Compositions
| Element | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon, C | ≤ 0.18 |
| Silicon, Si | 0.10 – 0.50 |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.90 – 1.60 |
| Phosphorus, P | ≤ 0.035 |
| Sulfur, S | ≤ 0.035 |
| Nitrogen, N | ≤ 0.012 |
| Copper, Cu | ≤ 0.35 |
| Chromium, Cr | ≤ 0.20 |
| Nickel, Ni | ≤ 0.40 |
| Molybdenum, Mo | ≤ 0.08 |
| Vanadium, V | ≤ 0.10 |
Physical Properties
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.8 g/cm³ | 0.282 lb/in³ |
| Melting Point | 1510 °C | 2750 °F |
| Boiling Point | – | – |
| Thermal Conductivity | 50 W/m·K | 29 Btu·ft/(h·ft²·°F) |
| Electrical Conductivity | 6.99 × 10⁶ S/m | 12.1 % IACS |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 486 J/kg·K | 0.116 Btu/(lb·°F) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 12 x 10⁻⁶ /°C | 6.7 x 10⁻⁶ /°F |
| Electrical Resistivity | 1.43 x 10⁻⁷ Ω·m | 8.6 x 10⁻⁷ Ω·in |
Mechanical Properties
AC (Air Cooled) Sate
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 490 – 620 MPa | 71 – 90 ksi |
| Yield Strength | ≥ 355 MPa | ≥ 52 ksi |
| Brinell Hardness HB | 170 – 220 | 170 – 220 |
| Rockwell Hardness HRB | 80-95 | 80-95 |
| Vickers Hardness HV | 180 – 240 | 180 – 240 |
| Elongation | 21% (in 200 mm) | 21% (in 8 in) |
| Elastic Modulus | 210 GPa | 30.5 msi |
QT (Quenched & Tempered) State
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 490-620 MPa | 71-90 ksi |
| Yield Strength | 355 MPa | 51.5 ksi |
| Elongation | 21% | 21% |
| Reduction of Area | 50% (typically) | 50% (typically) |
| Impact Absorption Energy | 34 J at -20°C | 25 ft·lbf at -4°F |
| Elastic Modulus | 200 GPa | 29 msi |
Industries & Applications
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Shipbuilding | Hull structures, Deck plating, Bulkheads, Keels |
| Offshore Structures | Oil rig platforms, Subsea pipelines, Wind turbine foundations, Support frames |
| Bridge Construction | Main bridge girders, Suspension cables, Bridge deck panels, Arch ribs |
| Heavy Machinery | Excavator arms, Crane booms, Bulldozer blades, Forklift frames |
| Automotive | Chassis components, Frame rails, Suspension arms, Crossmembers |
| Construction | Structural beams, Column supports, Reinforcement bars, Steel pilings |
| Pressure Vessels | Boiler shells, Reactor vessels, Heat exchangers, Storage tanks |
| Energy | Wind turbine towers, Power plant boilers, Solar panel mounts, Turbine casings |
Machining
Heat Treatment
- Normalizing: Heat to 900-940°C, hold for 1 hour per inch, air cool.
- Annealing: Heat to 830-870°C, hold for 1 hour per inch, furnace cool to 600°C, air cool.
- Hardening: Heat to 880-920°C, hold for 1 hour per inch, quench in water or oil.
- Tempering: Heat to 540-680°C, hold for 1 hour per inch, air cool.
- Stress Relieving: Heat to 600-650°C, hold for 1 hour per inch, air cool.
Surface Finish
- Shot Blasting: Cleans and prepares surfaces using abrasive material, making them ready for coating and improving adhesion.
- Sand Blasting: Uses sand particles to clean and roughen surfaces, suitable for various applications.
- Pickling and Passivation: Chemical treatment removes contaminants and rust, enhancing corrosion resistance and creating a smooth surface.
- Polishing: Uses abrasive material to make surfaces smooth and shiny, often for aesthetic purposes.
- Electroplating: Applies a metal coating using electric current to improve corrosion resistance and appearance.
- Painting and Coating: Adds a protective layer to prevent corrosion and enhance durability and appearance.
*Customization is available upon request.
Disclaimer
The provided heat treatment and surface treatment processes are general guidelines. Actual conditions may vary depending on specific applications and requirements. It is recommended to consult with a professional metallurgist or material scientist to tailor the processes to your particular needs. The information herein is not a substitute for professional advice and should not be relied upon as such.
Our Service
SteelPRO Group – manufacturer and solution provider for special steel, offering multi-industry application solutions and customised services, 100% quality free, accompanying customers in their growth!
Our Quality Control
- Roundness
- Tolerance
- Microstructure
- Non-Destructive Testing
- Destructive Testing
- Process Control
Service Integration Processing
- Welding
- Metal Fabrication
- CNC Machining
- Lathe
- Forming
QUESTION 1
QUESTION 2
QUESTION 3
QUESTION 4
QUESTION 4
CONTACT
CONTACT
Certifications






Other Products
-

-

SteelPRO Group offers FH550 high-strength structural steel plates for shipbuilding....
-

SteelPRO Group offers DH550 high-strength shipbuilding steel plates in stock....
-

SteelPro Group offers FH36 high-strength steel for shipbuilding. It has...

















